In the ever-evolving world of drone photography, one crucial element that significantly impacts image quality is the sensor size.
Drone camera sensors come in various sizes, each with its own set of advantages and limitations.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore drone camera sensor sizes, their significance, and how they influence the quality of your aerial imagery.
Understanding Drone Camera Sensors
Drone camera sensors are the electronic components responsible for capturing light and converting it into digital images or videos.
These sensors come in different physical sizes, typically measured in millimeters. The size of the sensor plays a pivotal role in determining how much light the camera can capture and how it interprets that light.
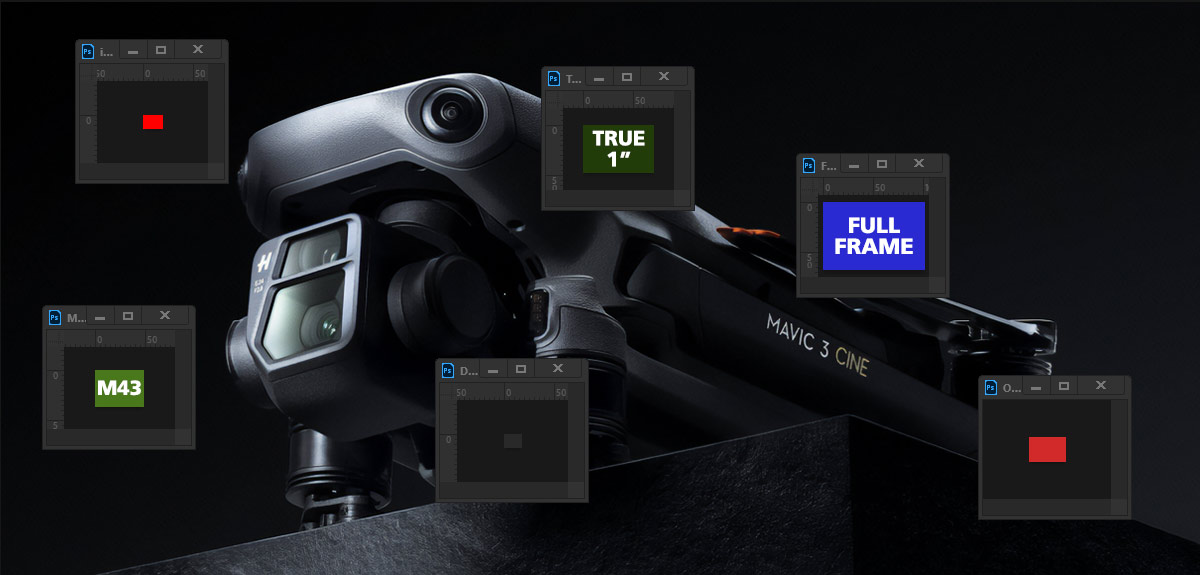
Common Drone Camera Sensor Sizes
a. 1/3-inch and 1/4-inch Sensors: These are among the smallest sensor sizes found in drones, commonly used in entry-level models. While they are compact and cost-effective, they tend to struggle in low-light conditions and may produce images with noticeable noise.
b. 1/2.3-inch Sensor: Slightly larger than the 1/3-inch and 1/4-inch sensors, the 1/2.3-inch sensor offers improved image quality and is found in many mid-range consumer drones. It strikes a balance between size, cost, and performance.
c. 1-inch Sensor: This sensor size is often considered the sweet spot for drone photography. It’s significantly larger than the smaller sensors, allowing for better low-light performance, higher dynamic range, and improved image quality. Many professional and high-end consumer drones feature a 1-inch sensor.
d. Micro Four Thirds Sensor: Some advanced drones are equipped with Micro Four Thirds sensors, which are even larger than 1-inch sensors. These sensors provide exceptional image quality, especially in challenging lighting conditions, and are often favored by professional photographers and filmmakers.
e. APS-C and Full-Frame Sensors: While less common, some specialized drones feature APS-C or full-frame sensors, which are equivalent to those found in high-end DSLR cameras. These sensors offer unparalleled image quality but are typically found in specialized, industrial, or custom-built drones.
Impact on Image Quality
The size of the sensor directly affects image quality in several ways:
a. Low-Light Performance: Larger sensors capture more light, resulting in better performance in low-light conditions. This reduces noise and allows for clearer, more detailed images.
b. Dynamic Range: Larger sensors typically have a wider dynamic range, preserving details in both shadow and highlight areas of an image.
c. Depth of Field: Bigger sensors can achieve a shallower depth of field, enabling more creative control over focus and background blur.
d. Overall Detail: Larger sensors tend to produce sharper and more detailed images, especially when paired with high-quality optics.
Conclusion
Understanding drone camera sensor sizes is crucial for making informed decisions when selecting a drone for your photography or videography needs.
Consider your budget, intended use, and the conditions in which you’ll be shooting to determine the sensor size that best aligns with your requirements.
Keep in mind that while larger sensors generally offer superior image quality, they may come at a higher cost and be featured in heavier and more expensive drone models.








Leave a Reply